Since the distant ancestor of man Homo Erectus stood up, humanity, in addition to all the possible advantages associated with walking upright (protection from wild animals, improved visibility, expanded work functionality), has received a set ofhaving musculoskeletal diseases. One of them is cervical osteochondrosis. Some people do not take the disease seriously, considering it an annoying but insignificant obstacle. This is especially true in situations where there is no severe pain.
Cervical osteochondrosis: causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention
Dizziness with cervical osteochondrosis is generally perceived as a separate symptom from the main disease, but as a result, the disease can lead to serious complications and even disability. In this article we will look at what drugs to take for dizziness with cervical osteochondrosis, learn how to get rid of dizziness with cervical osteochondrosis and analyze what exercises to do for dizziness with osteochondrosisof the cervix.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
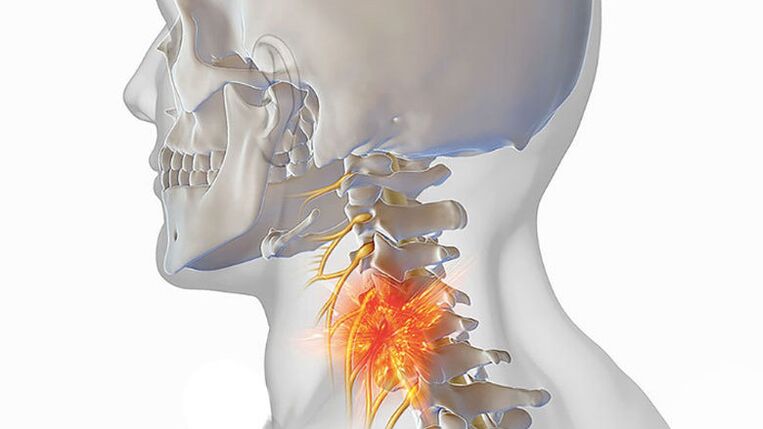
The term osteochondrosis comes from the ancient Greek words ὀστέον - "bone" and χόνδρος - "cartilage". Doctors use this term to define a group of dystrophic changes in joint cartilage caused by an increase in the volume of bone tissue. More than other joints, the cartilaginous seal between the vertebrae, which in medicine is called a "disc", suffers.
Osteochondrosis is divided by type into "cervical", "thoracic" and "lumbar". The cervix is more common. Today, this disease is a constant companion of every person over 40 years old. Despite the opinion that this disease develops over the years and young people do not suffer from it, modern medical practice proves the opposite, showing disappointing statistics in people over 30 years old.
Causes
The causes of osteochondrosis include direct ones (compression of vertebral vessels and nerves - compression of cervical vertebrae) and indirect ones related to the patient's lifestyle and physiological characteristics of his body.
Types of compression complications of osteochondrosis:
- Spondylolisthesis. Displacement of the spinal disc backwards or forwards. On a significant scale, displacement is fraught with paralysis and death.
- Osteophytes. Abnormal, pathological growth of bone tissue due to calcium salts.
- Extension. Intervertebral disc protrusion without rupture of the integrity of the collagen ring.
- Hernias. Nucleus displacement of the intervertebral disc with rupture of the collagen ring.
Reasons for compression:
- intense physical work;
- physical inactivity, "computer" disease, sedentary lifestyle;
- weight is higher than normal;
- metabolic disorder;
- genetic predisposition;
- wrong posture;
- weak tone of neck and back muscles in general;
- excessive strain, fatigue of back and neck muscles;
- a tendency to a certain position of the neck, for example, the habit of tilting the head to one side;
- "Old" injuries of the cervical spine;
- nervous breakdowns and stress.
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis
The main symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are sporadic and constant pain in the neck, upper shoulder girdle, collar and head. With advanced disease, vertigo (dizziness) and loss of consciousness are possible.
The complete symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are so different that the patient is often unable to independently identify one or another symptom with cervical osteochondrosis. Even the attending physician must perform a detailed examination in order to make an accurate diagnosis.
The symptoms of the disease vary according to its progress. Modern medicine distinguishes 4 stages of progression of osteochondrosis:
I – small changes in normal cervical lordosis. There may be slight pain when you turn your head. Slight discomfort when bending the neck;
II – small displacements between the vertebrae, torsion (uncoordinated rotation of the vertebra in relation to the spinal cord), reduction of the thickness of the intervertebral cartilage. Pain of mild to moderate intensity appears in the neck and head, tingling in the fingertips, tinnitus, when turning the head the patient hears a slight crackling;
III - the intervertebral cartilage is displaced by a quarter compared to the other, the thickness and size of the disc changes selectively, becomes thinner, changes its normal shape, the posterior osteophytes narrow the spinal canal, damaging the spinal cord. The pain becomes intense, its sporadic nature is lost, it becomes stable in nature, fluctuating from moderate to severe. Weakness appears in the hands, hearing is impaired. When you turn your head, the crackling sound is heard not only by the patient, but also by those around you. Possible loss of coordination of movements. By the way, dizziness with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is a very alarming sign, in which you should immediately consult a doctor if this has not already been done;
IV - intervertebral discs are significantly displaced, osteophytes and posterior protrusions become abnormally large, the spinal canal is significantly narrowed and curved, myelopathy is formed (syndrome of compression of the spinal cord and its vessels). Frequent dizziness, loss of consciousness. Strong and very strong pains in the neck, head, clavicle, shoulders. The face, tongue and palate become numb. Vision and hearing are significantly impaired. Weakness all over the body. Legs and arms are removed. Temporary paralysis of limbs. A very significant loss of coordination in space. Swallowing reflex disorder. Total loss of sensation in the hands and throughout the body.
Treatment and prevention of cervical osteochondrosis
When we ask the question "how to cure osteochondrosis of the neck? ", we must remember that with cervical osteochondrosis, the treatment must be on time, there is no way to delay it.
Therapeutic and preventive measures are closely related to each other in the treatment of osteochondrosis of the neck. Conventionally, the difference between them lies in the severity of the disease. Prevention of osteochondrosis is implemented before the onset of the disease and during its first three stages. Treatment of the disease begins from the moment of its appearance.
In this section we will find out whether it is possible to immediately eliminate many of the unpleasant symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis, what exercises can be done for dizziness with cervical osteochondrosis, which tablets, medicines and folk remedies are most often usedthe best for complicated osteochondrosis, how to treat dizziness, how to treat dizziness with cervical osteochondrosis, osteochondrosis with folk remedies.
Preventing
Eliminates many signs of osteochondrosis immediately. Includes four types of therapy:
- The traditional way to remove the signs of cervical osteochondrosis and vertigo is to constantly lead a healthy lifestyle;
- physical therapy (not recommended already in the third stage of the development of osteochondrosis, although the final decision rests with the vertebrologist);
- massage and self-massage (although manual therapy is very effective for cervical osteochondrosis and relieves pain, it is not recommended in the last stages of the disease);
- apply orthopedic advice and orthopedic equipment (Kuznetsov applicator, furniture, household items) in everyday life.
ethnoscience
Osteochondrosis of the neck can be treated at home using traditional medicine. The products she created are a creative combination of herbs, essential oils, fats, poisons, roots of various plants with alcohol and iodine.
Can a traditional medicine relieve dizziness and pain? Here the situation is the same as in the case of drug treatment - the pain can go away almost immediately, the prevention of dizziness will take some time. Treatment with traditional medicine should be started as soon as possible, then it will definitely bring a positive result.

























